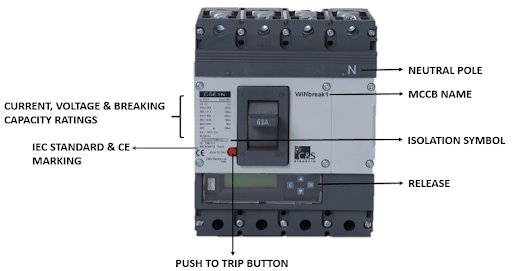
A circuit breaker is a switching device which also offers protection against short circuit. Unlike a fuse, the circuit breaker does not blow off but trips whenever there is a fault. The circuit breaker complies with IEC 60947-2 & can offer protection up to 150KA even beyond that, also a circuit breaker can offer a no of protections such as against:
Overload
Short Circuit
Under Voltage
Neutral
Earth Fault
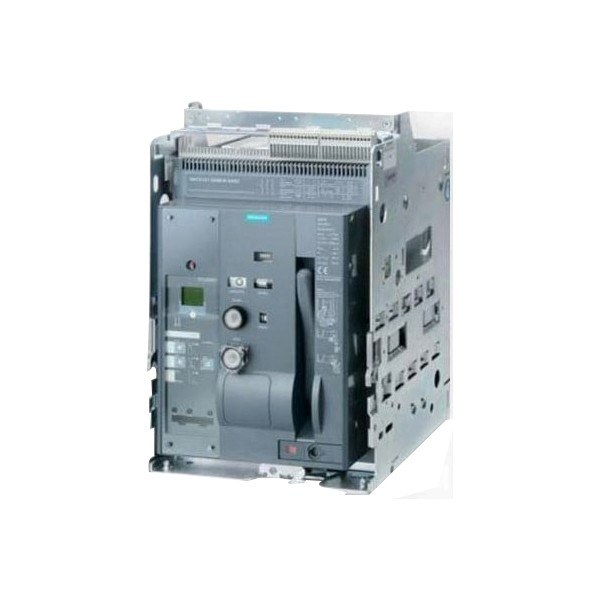



A circuit breaker is not required to be replaced after tripping once, instead it must complete its total no of operations as declared by the manufacturer. The tripping time for the circuit breaker may vary w.r.t its type, for example. the trip time for MCCB is less than 10ms & the opening time for ACB shall be less than 30ms. Not only this, but MCCB also has a dedicated position for tripping, whenever the MCCB trips, but its actuator lever also comes in between i.e. neither in ‘ON’ nor in ‘OFF’ position.
According to the medium of arc quenching, the circuit breaker can be differentiated as below
|
SNO |
MEDIUM OF ARC QUENCHING |
CIRCUIT BREAKER |
|
1 |
AIR |
ACB, MCCB |
|
2 |
VACUUM |
Vacuum Circuit Breaker |
|
3 |
GAS |
SF6 Circuit Breaker |
|
4 |
OIL |
Oil Circuit Breaker |
method of tripping, the circuit breaker can be below types
|
SNO |
METHOD OF TRIPPING |
CIRCUIT BREAKER |
|
1 |
BIMETAL (for Overload) & Armature (for Short Circuit) |
Thermal Magnetic Type |
|
2 |
ELECTRONIC |
Microprocessor Type |