A busbar is designed and accordingly manufactured, sufficiently rigid to efficiently support its own weight, and numerous forces imposed by mechanical vibration and also the electromechanical forces provided during a short circuit. The insulated busbars are totally enclosed in metallic enclosures of GI or Aluminum.
Used in a variety of configurations, busbars come in a multitude of shapes and sizes such as solid bars, flat strips, or rods and are commonly composed of copper, aluminum, and brass. Their cross-sectional size and material composition determine the amount of current that can be safely carried by the busbar.
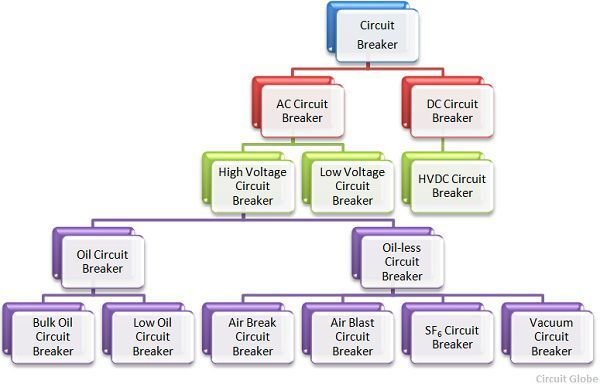
Types of Electrical Bus bar System
Single Bus-Bar Arrangement. ...
Single Bus Bar Arrangement with Bus Sectionalizing. ...
Main and Transfer Bus Arrangement. ...
Double Bus Double Breaker Arrangement. ...
Sectionalized Double Bus Arrangement. ...
One-and-a-Half Breaker Arrangement. ...
Ring Main Arrangement. ...
Mesh Arrangement.
When selecting busbars, be sure to check its maximum temperature, amp rating, size, and VAC rating. It is equally important to determine whether you need to purchase an enclosure or a cover for the busbar system.
Applications of Busbar
Some of the basic applications of Busbars include:
Industries
Hospitals
Power Plants
Data centers
Laboratories
Apartments
Retail facilities
Institutions
Metros
Railways
Technology settings
Busbars are popular because of:
Reduced Facility Costs: The installation of busbars is comparatively less expensive and there are no outside labor costs for electrical specialists. They don’t require routine maintenance and are less costly for remodeling or expansion.
Easy and Faster Installation: Busbars are installed easily and quickly with no downtime.
Environmentally Friendly: Depending upon the type, the busbars require only a few installation materials, and plug-in outlets are reusable and re-locatable.
Secure & Reliable: It replaces the cable distribution system which has its own complication for a fire hazard.