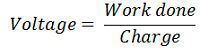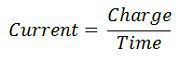Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Stationary Wave | Progressive Wave |
|---|---|---|
| Also called | Standing wave | Traveling wave |
| Basic | Energy is confined within the medium. | The transfer of energy from a location to another within the medium takes place. |
| Molecular vibration | Each particle of the wave exhibits different vibration at the same instant of time | Each particle of the wave possesses similar vibration at a different instant of time. |
| Amplitude characteristic of particles | Different | Same |
| Motion | Not transferable among the particles. | Easily transferred among the particles. |
| Velocity at mean position | All particles have their own maximum velocity. | All particles have similar maximum velocity. |
| Crests and Troughs | The crests and troughs of the waveform appear and disappear at the initial position. | The crests and troughs of the waveform move in the forward direction. |
| Wavelength | Double the distance present between 2 consecutive nodes or anti-nodes. | The distance between the point of similar phase at the similar time instant. |