Table of Electrical Symbols
| Symbol | Component name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Symbols | ||
| Electrical Wire | A conductor of electrical current | |
| Connected Wires | Connected crossing | |
| Not Connected Wires | Wires are not connected | |
| Switch Symbols and Relay Symbols | ||
| SPST Toggle Switch | Disconnects current when open | |
| SPDT Toggle Switch | Selects between two connections | |
| Pushbutton Switch (N.O) | Momentary switch - normally open | |
| Pushbutton Switch (N.C) | Momentary switch - normally closed | |
| DIP Switch | DIP switch is used for onboard configuration | |
| SPST Relay | Relay open / close connection by an electromagnet | |
| SPDT Relay | ||
| Jumper | Close connection by jumper insertion on pins. | |
| Solder Bridge | Solder to close connection | |
| Ground Symbols | ||
| Earth Ground | Used for zero potential reference and electrical shock protection. | |
| Chassis Ground | Connected to the chassis of the circuit | |
| Digital / Common Ground | ||
| Resistor Symbols | ||
| Resistor (IEEE) | Resistor reduces the current flow. | |
| Resistor (IEC) | ||
| Potentiometer (IEEE) | Adjustable resistor - has 3 terminals. | |
| Potentiometer (IEC) | ||
| Variable Resistor / Rheostat (IEEE) | Adjustable resistor - has 2 terminals. | |
| Variable Resistor / Rheostat (IEC) | ||
| Trimmer Resistor | Preset resistor | |
| Thermistor | Thermal resistor - change resistance when temperature changes | |
| Photoresistor / Light dependent resistor (LDR) | Photo-resistor - change resistance with light intensity change | |
| Capacitor Symbols | ||
| Capacitor | Capacitor is used to store electric charge. It acts as short circuit with AC and open circuit with DC. | |
| Capacitor | ||
| Polarized Capacitor | Electrolytic capacitor | |
| Polarized Capacitor | Electrolytic capacitor | |
| Variable Capacitor | Adjustable capacitance | |
| Inductor / Coil Symbols | ||
| Inductor | Coil / solenoid that generates magnetic field | |
| Iron Core Inductor | Includes iron | |
| Variable Inductor | ||
| Power Supply Symbols | ||
| Voltage Source | Generates constant voltage | |
| Current Source | Generates constant current. | |
| AC Voltage Source | AC voltage source | |
| Generator | Electrical voltage is generated by mechanical rotation of the generator | |
| Battery Cell | Generates constant voltage | |
| Battery | Generates constant voltage | |
| Controlled Voltage Source | Generates voltage as a function of voltage or current of other circuit element. | |
| Controlled Current Source | Generates current as a function of voltage or current of other circuit element. | |
| Meter Symbols | ||
| Voltmeter | Measures voltage. Has very high resistance. Connected in parallel. | |
| Ammeter | Measures electric current. Has near zero resistance. Connected serially. | |
| Ohmmeter | Measures resistance | |
| Wattmeter | Measures electric power | |
| Lamp / Light Bulb Symbols | ||
| Lamp / light bulb | Generates light when current flows through | |
| Lamp / light bulb | ||
| Lamp / light bulb | ||
| Diode / LED Symbols | ||
| Diode | Diode allows current flow in one direction only - left (anode) to right (cathode). | |
| Zener Diode | Allows current flow in one direction, but also can flow in the reverse direction when above breakdown voltage | |
| Schottky Diode | Schottky diode is a diode with low voltage drop | |
| Varactor / Varicap Diode | Variable capacitance diode | |
| Tunnel Diode | ||
| Light Emitting Diode (LED) | LED emits light when current flows through | |
| Photodiode | Photodiode allows current flow when exposed to light | |
| Transistor Symbols | ||
| NPN Bipolar Transistor | Allows current flow when high potential at base (middle) | |
| PNP Bipolar Transistor | Allows current flow when low potential at base (middle) | |
| Darlington Transistor | Made from 2 bipolar transistors. Has total gain of the product of each gain. | |
| JFET-N Transistor | N-channel field effect transistor | |
| JFET-P Transistor | P-channel field effect transistor | |
| NMOS Transistor | N-channel MOSFET transistor | |
| PMOS Transistor | P-channel MOSFET transistor | |
| Misc. Symbols | ||
| Motor | Electric motor | |
| Transformer | Change AC voltage from high to low or low to high. | |
| Electric bell | Rings when activated | |
| Buzzer | Produce buzzing sound | |
| Fuse | The fuse disconnects when current above threshold. Used to protect circuit from high currents. | |
| Fuse | ||
| Bus | Contains several wires. Usually for data / address. | |
| Bus | ||
| Bus | ||
| Optocoupler / Opto-isolator | Optocoupler isolates connection to other board | |
| Loudspeaker | Converts electrical signal to sound waves | |
| Microphone | Converts sound waves to electrical signal | |
| Operational Amplifier | Amplify input signal | |
| Schmitt Trigger | Operates with hysteresis to reduce noise. | |
| Analog-to-digital converter (ADC) | Converts analog signal to digital numbers | |
| Digital-to-Analog converter (DAC) | Converts digital numbers to analog signal | |
| Crystal Oscillator | Used to generate precise frequency clock signal | |
| ⎓ | Direct current | Direct current is generated from constant voltage level |
| Antenna Symbols | ||
| Antenna / aerial | Transmits & receives radio waves | |
| Antenna / aerial | ||
| Dipole Antenna | Two wires simple antenna | |
| Logic Gates Symbols | ||
| NOT Gate (Inverter) | Outputs 1 when input is 0 | |
| AND Gate | Outputs 1 when both inputs are 1. | |
| NAND Gate | Outputs 0 when both inputs are 1. (NOT + AND) | |
| OR Gate | Outputs 1 when any input is 1. | |
| NOR Gate | Outputs 0 when any input is 1. (NOT + OR) | |
| XOR Gate | Outputs 1 when inputs are different. (Exclusive OR) | |
| D Flip-Flop | Stores one bit of data | |
| Multiplexer / Mux 2 to 1 | Connects the output to selected input line. | |
| Multiplexer / Mux 4 to 1 | ||
| Demultiplexer / Demux 1 to 4 | Connects selected output to the input line. | |
| Name | Electrical Symbol | Alternate Symbol | Description |
| ground/earth | 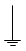 | This symbol identifies an earth(ground) terminal used for a zero potential reference point and electrical shock protection. | |
| equipotential | 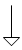 | 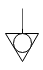 | It is a symbol to identify parts with the same voltage (i.e., the same electrical potential or equipotential). Since equipotential surfaces all have the same voltage, you won't be shocked if you touch two such surfaces unless you are also touching another part with a different potential from the first two parts. |
| chassis ground | 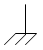 | It is a link between different metallic parts of a machine to ensure an electrical connection between them. It must not be considered as a link to the earth. | |
| battery | It is a device that consists of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections to empower electrical devices and generates constant voltages. | ||
| resistor | 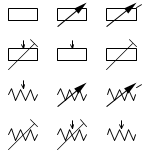 | It is an electrical component that reduces the electric current, for example, to limit the current passing through an LED. A resistor is used with a capacitor in a timing circuit. | |
| attenuator | It is an electronic device that reduces the power of a signal with appreciably distorting its waveform, which is the opposite of an amplifier. | ||
| capacitor |  | It is a device with two terminals, which stores electric energy. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. It can also be used as a filter to block DC signals but pass AC signals. | |
| accumulator |  | It is an energy storage device that accepts, stores, and releases energy, increasing or relieving pressure in the system. | |
| antenna | An antenna also knows as an aerial, is a device designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic (e.g., TV or radio) waves. | ||
| loop antenna | A loop antenna is a radio antenna consisting of a loop (or loops) of wire, tubing, or other electrical conductors with its ends connected to a balanced transmission line. | ||
| crystal | A crystal oscillator uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal of piezoelectric material to create an electrical signal with an exact frequency. | ||
| circuit breaker | A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. | ||
| fuse | A fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. | ||
| ideal source | An ideal voltage source is a two-terminal device that maintains a fixed voltage drop across its terminals. It is often used in the simplified analysis process of a real electric circuit. | ||
| generic component | |||
| transducer |  | A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Usually, a transducer converts a signal in one type of power to a signal in another. | |
| inductor |  | A coil of wire creates a magnetic field when current passes through it. It may have an iron core inside the coil. It can be used as a transducer converting electrical energy to mechanical energy by pulling on something. It is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in a magnetic field. | |
| half inductor | |||
| pickup head | 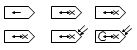 | ||
| pulse | |||
| saw tooth | |||
| step function | |||
| explosive squib | Explosive squib is often used on stage and film to trigger various special effects. | ||
| sensing link squib | |||
| squib igniter | |||
| surge protectors | 
| Surge protectors protect your electronics from power surges in your electrical system. | |
| instrument |  | For example, a voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring the electrical potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. The wattmeter is an instrument for measuring the electric power in watts of any given circuit. | |
| material | 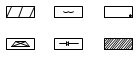 | ||
| delay element |  | The delay element provides a specified delay between the actuation of the propellant-actuated devices. | |
| permanent magnet | A permanent magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. | ||
| magnet core | |||
| ferrite core | |||
| igniter plug | |||
| bell | 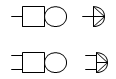 | The electric bell is found in an ordinary house doorbell, and when activated, it makes a ringing sound. | |
| buzzer | An electrical buzzer is similar to the bell that makes a constant buzz noise instead of a single tone or bell sound. | ||
| thermal element | |||
| thermocouple | 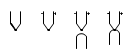 | ||
| thermopile | |||
| lamp | 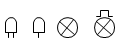 | A transducer converts electrical energy to light, used for a lamp providing illumination, for example, a car headlamp or torch bulb. | |
| fluorescent lamp | |||
| speaker | A speaker can take digital input and turn it into analog sound waves—one of the most important parts of a wide range of electrical products like TVs and telephones. | ||
| microphone | 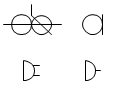 | ||
| oscillator | It produces a repetitive electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave. | ||
| AC source | Alternating Current, continually change direction. | ||
| DC source | 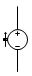 | Direct Current, always flow in one direction. |
Electrical wiring construction including outlets, switches, and lamps.










No comments:
Post a Comment