Learning
Objectives
➣ Capacitor
➣
Capacitance
➣
Capacitance of an
Isolated Sphere
➣
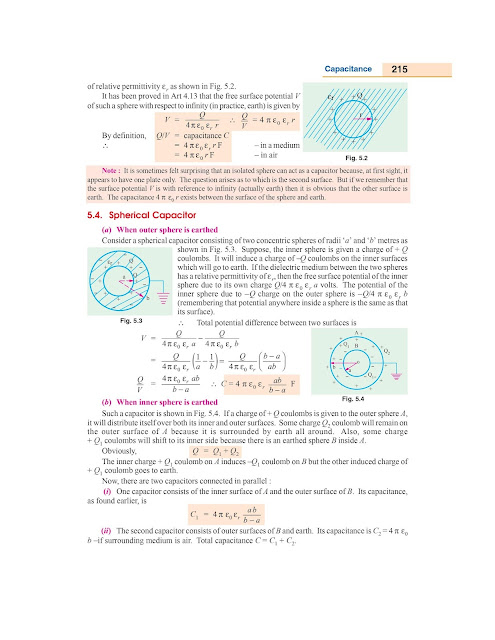
Spherical Capacitor
➣
Parallel-plate Capacitor
➣ Special
Cases of Parallel- plate Capacitor
➣
Multiple and Variable
Capacitors
➣ Cylindrical Capacitor
➣ Potential Gradient in Cylindrical Capacitor
➣
Capacitance Between two
Parallel Wires
➣
Capacitors in Series
➣ Capacitors in Parallel
➣
Cylindrical
Capacitor with Compound Dielectric
➣ Insulation
Resistance of a Cable Capacitor
➣
Energy Stored in a Capacitor
➣ Force of
Attraction Between Oppositely-charged Plates
➣
Current-Voltage
Relationships
in a Capacitor
➣
Charging of a Capacitor
➣
Time Constant
➣
Discharging of a Capacitor
➣ Transient Relations during capacitor charging cycle
➣
Transient Relations during
Capacitor
Discharging Cycle
➣
Charging and Discharging
of a Capacitor with Initial
Charge
5.1.
Capacitor
A capacitor essentially consists
of two conducting surfaces separated by a layer of an insulating medium called dielectric. The conducting sur- faces may be in the form of either circular
(or rectangular) plates
or be of spherical or cylindrical shape. The purpose
of a capacitor is to store elec- trical energy by electrostatic stress in the dielectric (the word ‘condenser’ is a misnomer since a capacitor
does not ‘condense’ electricity as such, it
merely stores it).
A parallel-plate capacitor is shown in Fig. 5.1. One plate is joined to
the positive end of the supply
and the other
to the negative
end or is earthed.
It is experimentally found that in the presence of an earthed
plate B, plate A is capable
of withholding more charge than when B is
not there. When such a capacitor is put across a
battery, there is a momentary flow of electrons from A to B. As
negatively-charged electrons are withdrawn from A, it becomes positive
and as these electrons collect
on B, it becomes negative. Hence, a p.d. is established between plates A and
B. The transient flow of electrons
gives rise to charging
current. The strength
of the charging
Fig. 5.1
current
is maximum when the two plates are uncharged but it then decreases and finally
ceases when
p.d.
across the plates becomes slowly and slowly equal and opposite to the battery
e.m.f.
5.2.
Capacitance
The property of a capacitor to ‘store electricity’ may be called its capacitance.
As we may measure the capacity of a tank, not by
the total mass or volume of water it can hold, but by the mass in kg of water
required to raise its level by one metre, similarly, the capacitance of a
capacitor is defined as “the amount of charge required to create a
unit p.d. between its plates.”
Suppose we give Q coulomb of charge to one of the two plate
of capacitor and if a p.d. of V volts is established between
the two, then its capacitance is
Hence,
capacitance is the charge required per unit potential difference.
By definition, the unit of capacitance is
coulomb/volt which is also called farad (in honour of Michael Faraday)
\ 1 farad = 1 coulomb/volt
One farad is defined as the capacitance of a capacitor
which requires a charge of one coulomb to establish a p.d. of one volt
between its plates.
One farad is actually too large for practical purposes.
Hence, much smaller
units like microfarad (mF),
nanofarad (nF) and micro-microfarad (mmF) or picofarad (pF)
are generally employed.
1 mF = 10-9 F; 1 nF = 10-9 F ; 1 mmF or pF = 10-12F Incidentally, capacitance is that property of a capacitor which delays and change of voltage across it.













































No comments:
Post a Comment