| Definition | Difference between two points of an electric field | The flow of charges between two points |
| Unit | Volt | Ampere |
| Symbol | V | I |
| Formula | 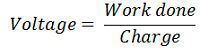 | 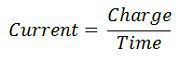 |
| Field Created | Magnetic Field | Electrostatic Field |
| Types | Alternating voltage & Direct voltage | Alternating Current and Direct Current |
| Polarity | Alternating voltage changes, but the direct voltage can not change its polarity. | Alternating current changes its polarity but the polarity of the direct current remains constant. |
| Produces | Alternator | Voltage |
| Measuring instrument | Voltmeter | Ammeter |
| Charges | 1 Volt = 1 Joule/ Coulomb | 1 Amperes = 1 coulomb /second |
| Series Connection | Unequal in all the components | Equally distributed in all the component |
| Parallel Connection | The magnitude of voltage remains same in all the component | The magnitude of current vary in all the components. |
| Loss | Due to impedance | Due to passive elements |
| Relation | It is the cause of the current | It is the effect of the voltage |
No comments:
Post a Comment